Abstract
Introduction: RNA splicing factor gene mutations are common in patients (pts) with myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS) and acute myeloid leukemia (AML) and portend a poor prognosis. RBM39, an RNA splicing factor, is required for the survival of AML cells with splicing factor mutations suggesting the potential for synthetic lethality. The anti-cancer sulfonamide E7820 degrades RBM39 and causes global disruption of mRNA splicing in vitro and in animal models of splicing factor mutant myeloid malignancies. Based on these pre-clinical data we designed an investigator-initiated phase II trial of E7820 to evaluate the safety, efficacy and the ability of E7820 to degrade RBM39 in pts with relapsed or refractory (R/R) splicing factor-mutant AML or MDS.
Methods: This phase II study (NCT05024994) enrolled adults with R/R myeloid malignancies with hotspot mutations in SF3B1, SRSF2, U2AF1, U2AF2, or a nonsense or frameshift mutation in ZRSR2 at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center and the Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center at the University of Miami. Pts received E7820 100mg daily until disease progression, relapse, toxicity, allogeneic stem cell transplant (allo-SCT), or death. Pts had to have adequate end organ function and ECOG performance status of ≤3. The primary endpoint was the objective response rate (ORR; defined as a composite of CR, CRh, and PR) within 6 cycles. Secondary and exploratory endpoints included an alternative definition of ORR (composite of CR, mCR, CRi, MLFS, PR, and HI), rates of event-free and overall survival (OS), and effects of E7820 on RBM39 protein degradation, gene expression, and RNA splicing. An optimal Simon 2-stage design was used with an unpromising and promising ORR of 10% and 30%, respectively, leading to the enrollment of 12 pts during stage I, the results of which are presented here. If >1 patient achieves an objective response, another 23 pts will be enrolled for a target enrollment of 35 pts.
Results: 12 pts were enrolled and treated (7 AML, 5 MDS) with a median age of 77 years (range [R] 71-85). Pts had received a median of 3 lines of prior therapy (R 1-6). Baseline patient and disease characteristics are shown in Table 1. At the time of data cut-off (7/14/2022), the median duration of treatment with E7820 was 2.5 cycles (range: 1-5 cycles) with 3 pts continuing to receive treatment.
At data cut-off, there were no protocol-defined responses. One MDS pt had a transient mCR without HI (blast reduction from 8% to 3%); all other pts had stable or progressive disease as their best response. No pts proceeded to allo-SCT. Median OS from E7820 initiation to death or last follow-up was 3.8 months (95% CI: 1.5 months - not reached).
E7820 was well-tolerated with diarrhea (5 pts; 42%), non-cardiac chest pain (3 pts; 25%) and falls (3 pts; 25%) as the most frequent treatment emergent adverse events (AEs). Hematologic toxicity was low with anemia (grade [G] 3), thrombocytopenia (G4), and neutropenia (G2 and G4) occurring in 1, 1, and 2pts, respectively. Overall, 9 pts (75%) experienced a G3/4 adverse event. Serious adverse events occurred in 6 pts (50%) including 1 G5 (cardiac arrest; unrelated to E7820) and 3 G4 events (neutropenia, hematoma, and respiratory failure). Among the 10 AEs with potential attribution to E7820, 4 were G3/4 (G4 neutropenia, G3 anemia, G3 epistaxis, G3 AST elevation). There were no treatment discontinuations due to study drug associated AEs.
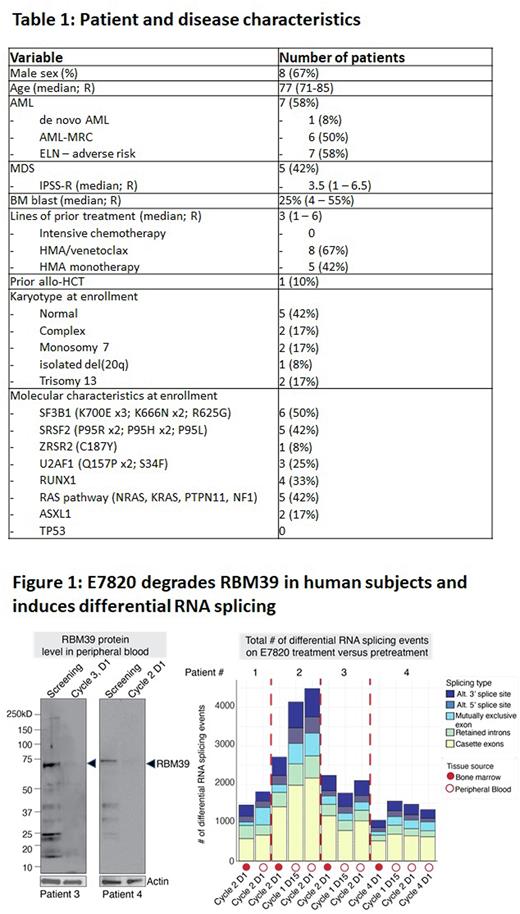
E7820 induced RBM39 degradation in the peripheral blood from patients and impaired RNA splicing in vivo (based on RNA sequencing) consistent with target engagement (Figure 1). At the same time, the degree of splicing inhibition in patients was less in magnitude in bone marrow compared to peripheral blood and nearly 50% less than that seen in AML cell lines treated with E7820 doses exhibiting preclinical efficacy.
Conclusions: In this phase II trial of E7820 in AML and MDS patients with splicing factor mutations, we found acceptable safety of E7820 monotherapy at the previously established maximum tolerated dose. Although the efficacy of E7820 was limited, evidence of target engagement combined with the tolerability of RBM39 degradation serves as a proof of concept that splicing factor mutant disease can be targeted in humans. Combination therapies of E7820 with standard of care agents and the use of newer generation RBM39 degraders are in development.
Disclosures
Stahl:Novartis: Other: Advisory Board; Boston Consulting: Consultancy; Curis Oncology: Consultancy. Taylor:Karyopharm, Inc: Honoraria. Chandhok:Servier: Consultancy. Hogg:AbbVie: Current Employment. Abdel-Wahab:Envisagenics Inc., AIChemy, Harmonic Discovery Inc., and Pfizer Boulder: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; H3B Biomedicine, LOXO Oncology, and Nurix Therapeutics: Research Funding; H3B Biomedicine, Foundation Medicine Inc, Merck, Prelude Therapeutics, and Janssen: Consultancy. Stein:Astellas Pharmaceutical, Agios Pharmaceuticals, and Genentech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Daiichi-Sankyo, Celgene Pharmaceuticals, and Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Auron Therapeutics: Current equity holder in private company; PinotBio, Bristol Myers Squibb, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, Foghorn Therapeutics, Blueprint Medicines, Gilead Sciences, Janssen Pharmaceuticals: Consultancy; PTC Therapeutics and Syros: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Syndax: Consultancy, Research Funding; Bayer: Research Funding; Amgen, AbbVie, Seattle Genetics, and Biotheryx: Consultancy.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal